Get a Handle on Windows Processes and Services for Better Anomaly Identification
Contents
Get a Handle on Windows Processes and Services for Better Anomaly Identification#
Whether you intend to use Windows 10 to run your samples or collect samples from a Windows 10 environment, it is crucial to be able to distinguish between normal and abnormal Windows 10 processes. Once you comprehend what is running and how it is running, it will be simpler to identify anomalies. While this post is not about Threat Hunting (check out Threat Hunting blog posts), where this approach could be extremely useful, we believe it will be useful for Malware Analysis.
It is preferable to use Sysinternals Process Explorer (procexp) when reviewing this section so that you can visualize the information. On the bottom are displayed a few of the Windows 10 processes that will be discussed in this section:
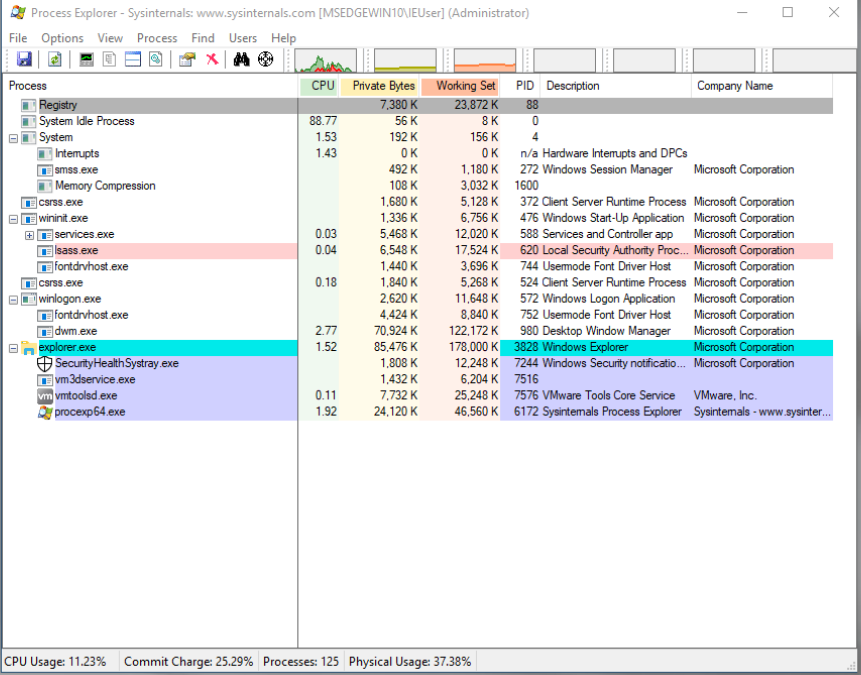
System Idle process - This is not truly a process and is used to track the idleness of the system’s CPU. This process has no parents and have PID: 0. No true image, cmd line, etc. Note that its created by ntoskrnl.exe. Always runs in kernel-mode. Number of threads represents the number of available CPUs: one thread for each CPU to keep it busy.
Windows Registry - Not truly a process. No parent (was 4 (system)). No image. In lieu of page pools, used for managing the Windows registry. Therefore, it serves as a cache for the Windows Registry in memory rather than on disk.
System process - There is no true image for this process too! This process also has no parents and have PID: 4. Childs: smss.exe, Memory Compression and Interrupts.
Note that:
Created by
ntoskrnl.exeRuns in kernel-mode only
Owns the sockets and handles to any file that the kernel opens
Processes ID are multiple of 4 with the value 4 belonging to system
You might be asking: Why did the System Process have a Process ID of 4 when the System Idle Process had 0?
Process IDs on Microsoft Windows are multiple of 4, with the value of 4 always belonging to System.
Windows interrupts - Interrupts is not truly a process. Parent: system. No image. Just used to measure the time required to service HW interrupts and deferred Procedure Calls.
Windows Memory Compression Process - Memory compression “Process”. Parent process is system. Used to store memory compression in its address space. Useful for systems with restricted assets.
Windows Session Manager Subsystem - smss.exe. Parent process is system and started by system. Childs: winlogon.exe. Image: C:\Windows\System32\smss.exe. Cmdline is SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe.
Notes that:
1st User-mode process
Responsible for initiating user sessions
At any given time, only one copy should exist!
Create session number one
Create session number zero (system services)
Begins during boot-up;
Initializes environment variables
Loads the subsystems
OS/2,POSIX, andWindows (Win32).Loads both the kernel and user modes of the
Win32subsystem:Win32k.sys(kernel mode) andwinsrv.dllandcsrss.exe(user mode)Creates
DOSdevice mappings (such asCOM,LPT1, and drive letters) that are listed atHKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\DOS Devices.Creates memory paging files for virtual memory
Windows Initializasion Process - wininit.exe. This is created by smss.exe but not the currently running copy. What happens is, another smss.exe creates this process then exits. (Parent dies). The child processes creates on Windows 10:
services.exelsass.exeFontdrvhost.exeIsm.exeLsaIso.exeWerFault.exe
Image is C:\Windows\System32\wininit.exe. Cmdline: wininit.exe.
Notes:
Creates the
%windir%\tempdirectoryDEPand High EntropyASLRenabledCheck Strings /Environment
Windows Service Control Manager (SCM) - Services.exe. Parent process is wininit.exe. Childs: svchost.exe (System and ShareHost Third-Party services), Third-Party Services Standalone .exe. Systen Scheduled Tasks set to run with system privileges and task action set to custom handler.
Cmdline is wininit.exe. Cwd: C:\Windows\System32.
Notes that:
SLR,DEP,CFGall enablesUsed to control services that run as background services and are not attached to a user session
SCM will either directly start the process or call
svchost.exewhich will host the service DLLS.Only one instance should be running at any given time
Runs under session 0
Windows Service Host Process - svchost.exe. Parent process is services.exe. What abouts childs? Many should adopt the blacklist method (cmd.exe and parent cmdline!=“*schedule*” may detect backdoor shell activity). Images is C:\Windows\System32\svchost.
Note that:
Multiple instances can be running
User should be one of three options:
NTAUTHORITY\SYSTEM
LOCAL SERVICE
NETWORK SERVICE
Must include
-k <name>, where<name>is a category key valuein the registry:
Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\currentVersion\SvhostAll instances should be running in session 0
Cmd Check:
tasklist /svc/ fi "IMAGENAME eq such"
Local Security Authentication Server - lsass.exe. Parent process winlogon.exe for pre-Vista Windows versions, and wininit.exe for post-Vista Windows versions. Image is C:\Windows\System32\lsass.exe. Cwd is C:\Windows\System32\.
Notes that:
Location of autostart is:
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\VaoHSVUtilizes session 0 (3e7)
In charge of enforcing the security policy, validating passwords, and generating access tokens.
Usually target for code injection
Receives the username and password captured by
winlogon.exefor authentication and checks to see if they match those stored in the registry or active directory.The
LSASSprocess callsNtCreateTokento generate an access token object containing the user’s security profile, and then sends it towinlogon.exe.
Windows Explorer - explorer.exe. Parent process is userinit.exe or winlogon.exe, but can be anything .exe using explorer.exe. Children processes: Anything started by interactively by a user session (e.g. firefox.exe or mspaint.exe) and programs set to autostart (RunKey and StartupFolder). Image is C:\windows\explorer.exe.
Notes that:
Parent will show as
<Non-existent Process>sinceuserinit.exeterminates itself.Autostarts from:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell
Windows Logon - winlogon.exe. Parent is “does not exist” since smss.exe exits. Childs processes are: dwm.exe, mpnotify.exe, fontdrvhost.exe, userinit.exe, PhotoScreensaver.scr and scrnsave.exe. Image and cmdline is C:\Windows\System32\winlogon.exe. Cwd: C:\Windows\System32\.
Notes:
Used for interactive user logon and logoff when SAS keystroke combinations (ctrl+alt) are employed. Processes
Ctrl+Alt+DelExecuted in session 1
Changes to files and directories protected by Windows File Protection are monitored
When credentials are required and the UI displays the logon dialog,
LogonUI.exemay be generated.winlogon.execan also call Network Provider DLLs if additional secure authentication is required.Secure Authentication Sequence (SAS)
is used to send the username and password to
LSASS.EXEvia LPC, and in return receives an access token object containing the user’s security profile. Then, under the registry keyHKLM\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon,winlogon.execalls the initial process (userinit.exeby default).
Windows Client/Server Runtime Subsystem - csrss.exe. No parent process. Image is C:\Windows\System32\csrss.exe.
Notes that:
User-mode process that is part of the windows32 subsystem.
Legacy process (from Windows NT)
Responsible for the Windows console
With
win32.syskernel-mode devices driver, plusconhost.exefor console windows, in addition to a variety of DLLs to convert Windows API calls to kernel mode system service calls.An idle process that monitors the CPU’s idle time using a single thread
Windows User Initialization Process - userinit.exe. Parent process is winlogon.exe. Childs are explorer.exe and cmd.exe (or a like) with cmd line containing “*\netlogon\*” (stuff set to autostart via NetLogon Share). Initializes the user environment, starts explorer.exe, and then exits. This is why explorer.exe is displayed without a parent. Note that winlogon.exe, the parent process of userinit.exe, does not terminate because it also handles system logoff.
Windows Local Security Authority Process - lssas.exe. Parent process is wininit.exe. Childs? Rare (exclude legit ones like passwordfilters and a like). Image is C:\Windows\system32\lsass.exe
References#
See also
Would you like to learn practical malware analysis techniques? Then register for our online course! MRE - Certified Reverse Engineer
