Run 32-Bit Windows-Based Applications on 64-Bit Windows with WOW64
Contents
Run 32-Bit Windows-Based Applications on 64-Bit Windows with WOW64#
Windows WOW64 is a subsystem of the Windows operating system that allows 32-bit applications to run on 64-bit Windows systems. WOW64 is included with all 64-bit versions of Windows and is transparent to the user, meaning that 32-bit applications will run as if they were native 64-bit applications. WOW64 provides compatibility with existing 32-bit applications and drivers, and also allows for the development of new 64-bit applications that can take advantage of the increased performance and security of 64-bit Windows. In this article we explain how WOW64 works and why it matters in fields such as Malware Analysis.
What is WoW64?#
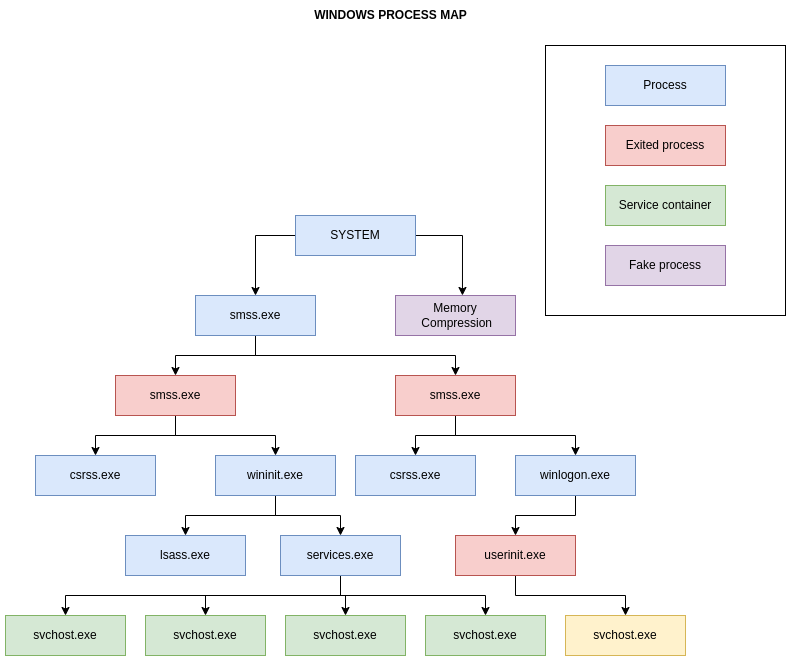
In the picture above we cover only main processes.
Windows 32-bit on Windows 64-bit, sometimes known as WoW64, is a component of the Windows operating system that allows 32-bit applications to operate on Windows 64-bit.
In other words, it is a technology that enables 32-bit applications to operate on 64-bit Windows without the application being aware that it is operating in an emulated environment.
WoW64 Main Components and Layout
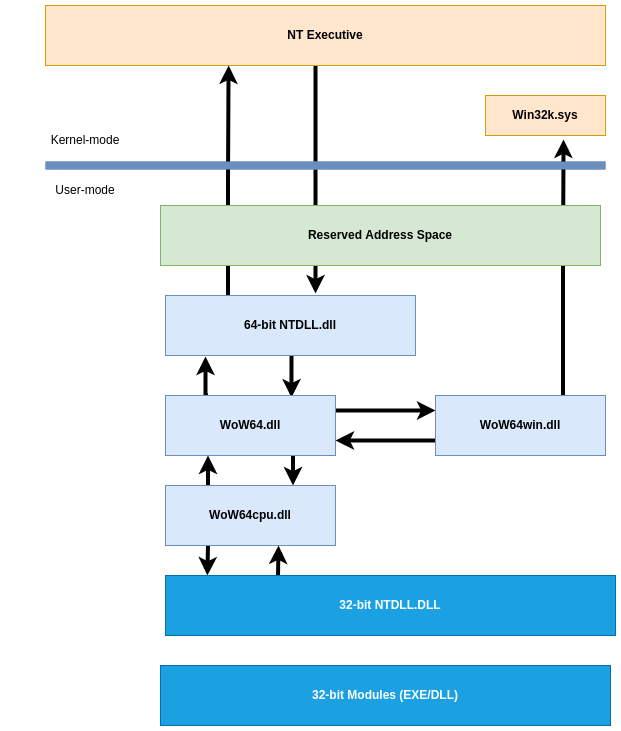
As we saw in the previous layout figure, the WOW64 emulator runs in user mode. WoW64 is an interface between the 32-bit version of Ntdll.dll and the kernel of the processor, and it intercepts kernel calls.
WOW64 emulator DLLs consists of:
Wow64.dllis the basic emulation infrastructure and the entry-point routines forNtoskrnl.exe.Wow64Win.dllprovides entry-point function thunks forWin32k.sys.Wow64Cpu.dll(only forx64): enables the execution ofx86programs onx64.
These DLLs, along with the Ntdll.dll (64-bit version), are the only 64-bit binaries that can be loaded into a 32-bit process.
There will be two sets of Executables and DLLs on a Windows 64-bit System:
C:\Windows\System32-> Native64-bitC:\Windows\SysWoW64->32-bitimages
According to the preceding statement, native Windows 64-bit executables and DLLs can be found in the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
Consequently, cmd.exe, notepad.exe, and any other executables executing from this path are native 64-bit images.
This is an example of Notepad (32-bit) running from SysWOW64 directory:
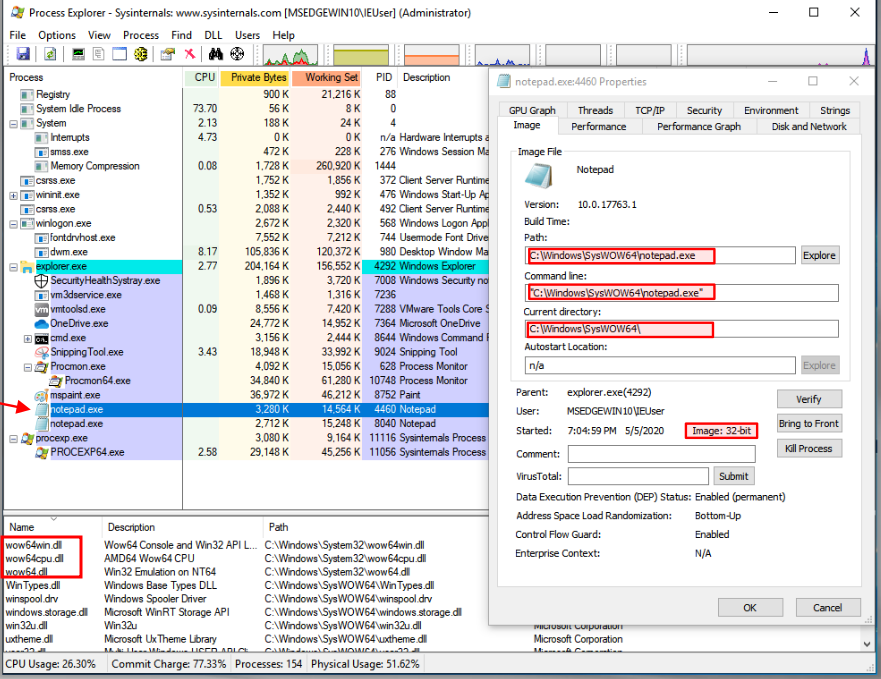
Also see the WoW64 subsystem files being loaded wow63win dll, wow64cpu.dll, and wow64.dll.
And this is Notepad (64-bit) running from System32 directory:
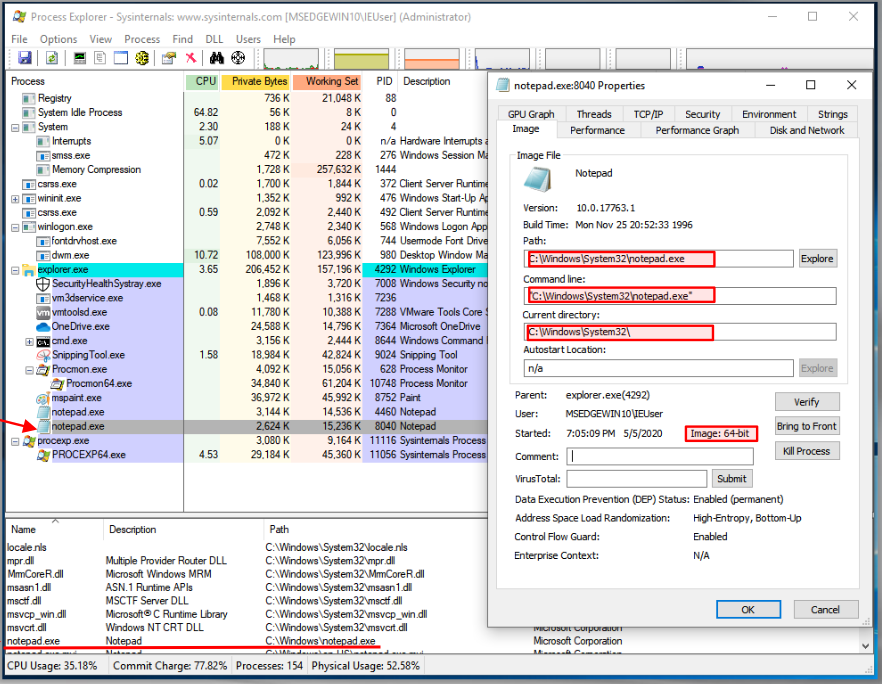
So you might be asking: Why all this redundancy in DLLs and EXEs?
This is due to the fact that 32-bit processes cannot load 64-bit DLLs, and vice versa. Also, as you recall from earlier posts, the pointer sizes and address ranges are different, which implies that without this emulation, they cannot function! The sole exception is DLLs containing only resources.
Also, if you check the 32-bit version, you will see that it has to load both the 32-bit and 64-bit version of NTDLL.dll because calls must be done using 64-bit version, so the 32-bit will pass them to the 64-bit, which is part of
how these processes work on a Windows 64-bit:
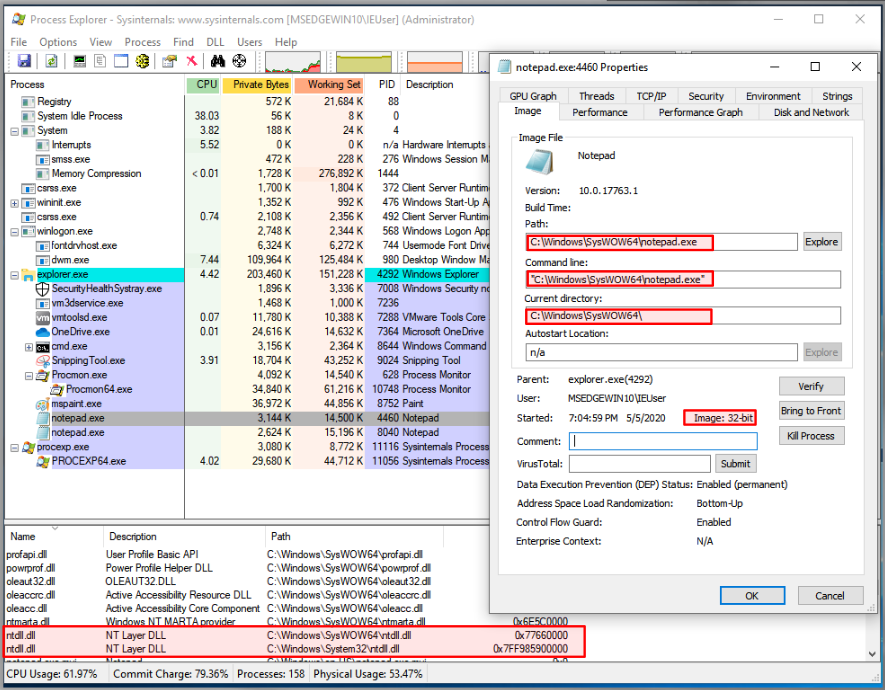
Check the addresses used for each of the NTDLL.dll pictures on the preceding image. The 32-bit version uses a 4-byte address, but the 64-bit uses an 8-byte address (8 bytes).
Note: The columns have been manually arranged to present the information you see. This is not how they are displayed by default.
WoW64 File System Redirections
WOW64 hides the fact that there is a different directory for
64-bit and 32-bit images by using a file system redirector. In most cases, whenever a 32-bit application attempts to access %windir%\System32, %windir%\lastgood\system32, or %windir%\regedit.exe, the access is redirected to an architecture-specific path.
Below is a list of examples what happens when a 32-bit x86 Process makes a request:
%windir%\System32(original) ->%windir%\SysWOW64- (redirected path for32-bit x86Processes)%windir%\lastgood\system32->%windir%\lastgood\SysWOW64%windir%\cmd.exe->%windir%\SysWOW64\cmd.exe
Note: Please check the exceptions! File redirection exceptions could happen if:
Access to display
UAChas special caseDirectories in the list below are also exempt from redirection:
%windir%\system32\catroot%windir%\system32\drivers\etc%windir%\system32\catroot2%windir%\system32\logfiles%windir%\system32\driverstore%windir%\system32\spool
But in Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: %windir%\system32\driverstore is redirected.
Also please check the Microsoft documentation for further details.
WoW64 Registry Redirector
Similar to the file system redirector, the registry also contains a redirector to isolate 32-bit and 64-bit applications by presenting distinct logical representations of specific registry sections.
Registry calls are intercepted and mapped to their proper logical registry views and physical registry locations.
The process of redirection is transparent to the application.
Redirected keys are mapped to physical locations under Wow6432Node.
For example, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINES\Software is moved to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node. However, the physical position of redirected keys should be considered reserved by the system, and applications should not directly access a key’s physical location because it may change.
Why are we discussing all of this?
Well if you are monitoring a 32-bit malware sample on a Windows 64-bit system and then you see the files, libraries, and registry locations being accessed are all different than what you might expect, now you know why.
Below is a list of other core Windows System files to keep an eye out for:
Ntdll.dllis a DLL with a specific purpose containing internal support routines and system-service dispatch stubs to executive functions. Through a process known as system service dispatching,Ntdll.dlltransfers incoming API calls to their appropriate kernel services.Kernel32.dllis commonly mistaken as the Windows kernel but is actually a user-mode DLL that simply passes on requests for the kernel tontdll.dll.
Note:
Kernel32.dll,Advapi32.dll,User32.dll,Gdi32.dllare core Windows subsystem DLLs
Ntoskrnl.exe- Executive and kernelHal.dll- HALWin32k.sys- kernel-mode part of the windows subsystem (GUI)Hvix64.exe- Intel HypervisorHvax64.exe- AMD Hypervisor.sysfiles in\systeRoot\System32\Driverscore driver files, such as DirectX, VolumeManager, TCP\IP, TPM, and ACPI support.
What is a System Service?
You would be surprised if we say, “It’s just a process”!
A service is identical to a process, with the exception that it often runs in the background and the user may not interact with it directly! That is, this is a background process.
Conclusion#
Malware authors could make their malware run as a service, so it is also essential to comprehend how it operates and how it is often configured. This topic will be discussed in greater depth in a subsequent post about “persistence mechanisms.”
Yes, all of them are Windows services operating in the background. There is no specific count for them, but they are numerous!
References#
WoW64 Implementation Details
Filesystem Redirector
Registry Redirector
See also
Would you like to learn practical malware analysis techniques? Then register for our online course! MRE - Certified Reverse Engineer
