How Practical is Homomorphic Encryption?
Contents
How Practical is Homomorphic Encryption?#
Homomorphic encryption is a form of encryption that allows for computation on ciphertexts, generating an encrypted result which, when decrypted, matches the result of the operations as if they had been performed on the plaintext. This type of encryption is useful for cases where it is desirable to be able to compute on data without decrypting it first, such as in cloud computing or database management. However, homomorphic encryption schemes are often slower and more resource-intensive than other schemes, and can be less secure in some cases.In this blog post, we will take a look at homomorphic encryption, what it is, and some of the benefits and drawbacks of this type of encryption.
Introduction#
Homomorphic encryption is a cybersecurity technique where data can be encrypted and then run through a mathematical transformation without being decrypted. This means that only the owner of the encryption key has access to the data.
Homomorphic encryption can be used for a variety of things, including cloud security and digital signatures. It’s also employed in data recovery and mathematical cryptology.
Homomorphic encryption is a type of data encryption that enables data manipulation without affecting the content. Individual chunks of data rather than complete files or messages can be encrypted and decrypted as a result. Homomorphic encryption has a wide range of uses, including internet security and healthcare.
How it works#
When compared to other encryption systems, where the user must first decrypt encrypted data before working on it. This creates vulnerabilities due to the possibility of data manipulation. This encryption methodology is more secure; it addresses this issue by allowing encrypted data to be analysed without being decrypted while remaining in its encrypted state.
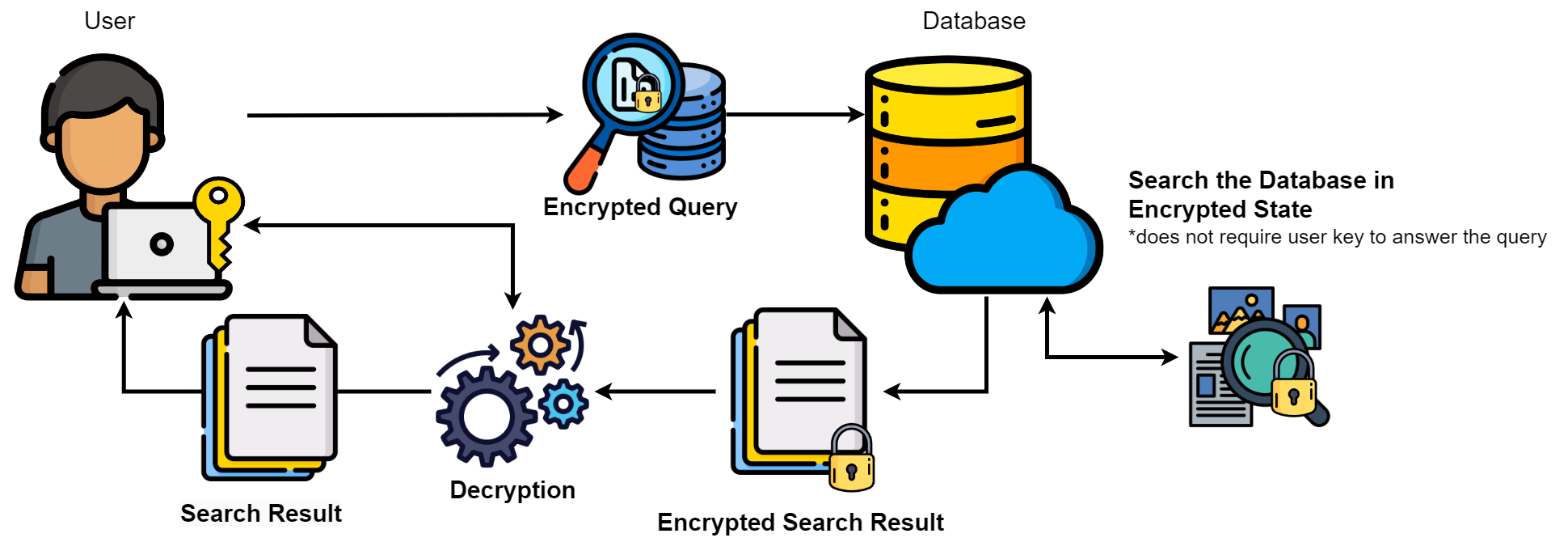
Benefits of Homomorphic Encryption#
The data is always encrypted, reducing the chances of sensitive data being exposed.
It eliminates the compromise between data usefulness and data privacy.
Homomorphic encryption schemes are malleable.
It is especially useful in industries that rely heavily on protecting users’ privacy, such as healthcare.
It is very useful in cloud migration and adoption.
It helps companies adhere to data regulations and compliance laws.
Types of Homomorphic Encryption#
1. Fully Homomorphic Encryption: Fully homomorphic encryption is sometimes considered the holy grail of homomorphic encryption, which ensures that data is safe and available. The strongest concept of homomorphic encryption is that it allows the assessment of unlimited circuits built of several types of gates of limitless depth. Fully homomorphic encryption refers to a cryptosystem that allows random ciphertext processing (FHE). This scheme allows the creation of programs with any desired functionality that can be performed on encoded inputs to produce encoded results. Because such a program does not need to decrypt its input, a third party can run it without revealing its input or internal state. Fully homomorphic cryptosystems have several practical implications, such as in cloud computing.
2. Partial Homomorphic Encryption: PHE is a cryptographic approach for securely computing certain functions on encrypted information. The effectiveness of partially homomorphic encryption systems is predicated on the notion that such functionalities are partial. Thus, indicating that only a part of the details about an input can be derived without decrypting the data,
3. Somewhat Homomorphic Encryption: The (Somewhat Homomorphic Encryption) family of cryptographic algorithms allows encryption and decryption without knowing the actual input. When only a fraction of the original data is required for decoding or authentication, this allows for more efficient data storage and transmission. It allows for limited procedures that can only be executed a certain number of times.
4. Levelled fully homomorphic encryption: LHE assesses unpredictable circuits made up of many kinds of gates with bounded depth.
Drawbacks to Homomorphic Encryption#
It is still slow, but with the premise of its secure methodology, businesses shouldn’t have to compromise slower business processes in exchange for security.
To make homomorphic functional, it still requires either application adjustments or dedicated and individualised application programs.
More technology companies are employing this encryption methodology while putting into consideration the repercussions of its drawbacks.
