Blockchain Technology
Contents
Blockchain Technology#
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary concept with the potential to transform various industries, and cybersecurity is no exception. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of blockchain technology, its applications in cybersecurity, and its potential benefits and challenges.
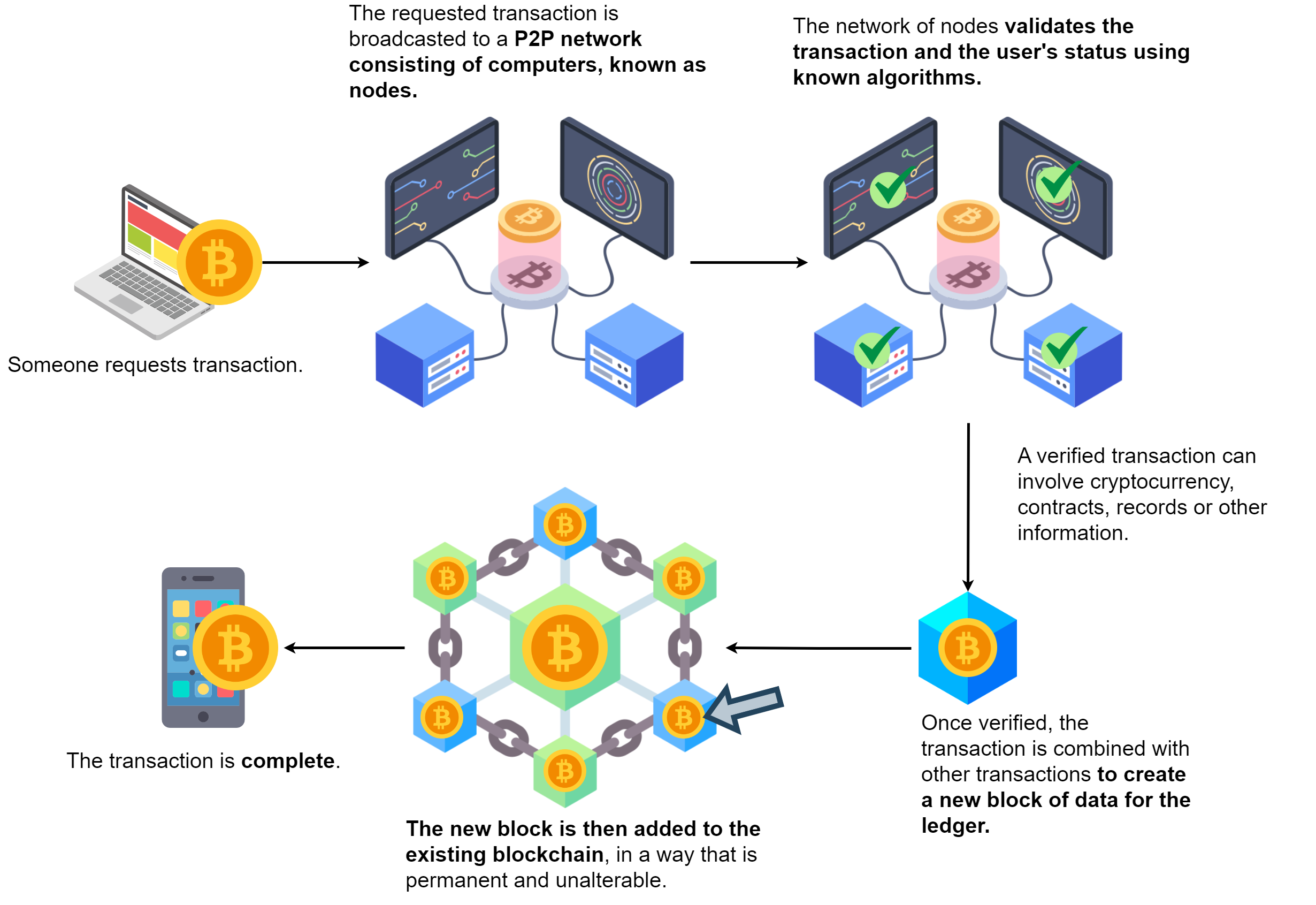
Understanding Blockchain Technology#
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology that enables the secure recording of transactions across a network of computers. Each recorded transaction is called a “block,” and these blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a “chain.” The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity has control over the entire chain, making it highly resistant to tampering and unauthorized modifications.
Key Components of Blockchain#
Blocks: Information is grouped into blocks, each containing a set of transactions. These blocks are linked together chronologically, forming a chain.
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network where no single entity has complete control. This decentralization enhances security by eliminating single points of failure.
Consensus Mechanisms: To ensure the integrity of transactions, blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms require participants to solve complex mathematical puzzles or stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency to validate transactions.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded in a block and added to the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or delete. This immutability provides a high level of data integrity.
Cryptography: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and ensure the integrity of data. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link between them.
Applications of Blockchain in Cybersecurity#
Blockchain technology offers several intriguing applications in the realm of cybersecurity, addressing challenges such as data integrity, authentication, and secure transactions.
Secure Data Storage and Integrity#
Blockchain can be utilized to create tamper-proof data storage systems. Any data recorded on the blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous block using cryptographic hashes. This ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without changing subsequent blocks, making it highly secure against unauthorized modifications.
Example: Storing sensitive medical records on a blockchain ensures that patient data remains confidential and cannot be tampered with. Only authorized parties with the appropriate cryptographic keys can access and update the records.
Authentication and Identity Management#
Blockchain can improve authentication and identity management processes by creating a decentralized, immutable record of identities. This can help combat identity theft and streamline verification procedures.
Example: Civic, a blockchain-based identity verification platform, allows users to securely prove their identity without exposing sensitive information. This can be used for activities such as online age verification or accessing financial services.
Supply Chain Security#
Blockchain can enhance supply chain security by providing end-to-end visibility and traceability. Each step of the supply chain can be recorded on the blockchain, ensuring that products’ origins and movements are transparent and tamper-proof.
Example: Walmart has implemented a blockchain-based system to track the journey of food products from farm to store shelves. This enables rapid identification and resolution of issues such as contaminated food outbreaks.
Decentralized DNS and DDoS Mitigation#
Traditional Domain Name System (DNS) is susceptible to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Blockchain-based DNS solutions distribute the system across multiple nodes, making it more resilient against such attacks.
Example: The Handshake project aims to create a decentralized DNS system that is resistant to censorship and DDoS attacks, ensuring the availability of websites even during cyberattacks.
Secure Transactions and Payments#
Blockchain technology can provide a secure platform for financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive payment information.
Example: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum use blockchain to enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, making them transparent and verifiable.
Challenges and Considerations#
While blockchain technology offers promising solutions to cybersecurity challenges, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations and potential drawbacks.
Scalability: Blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum have faced scalability issues, with limited transaction processing speeds and high energy consumption. As more transactions are added to the chain, the network can become slower and less efficient.
Regulatory and Legal Challenges: The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of blockchain presents challenges in terms of regulatory compliance, especially in industries that require strict identification and verification procedures.
Privacy Concerns: Although blockchain provides security through encryption, it is not inherently private. Transactions and data recorded on the blockchain are accessible to all participants, potentially leading to privacy concerns, especially in sensitive applications.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: While smart contracts offer automation and efficiency benefits, they can also be susceptible to vulnerabilities and bugs in the code. Flaws in smart contracts can lead to unintended consequences or even financial losses.
Final Insights: The Importance of Blockchain in Cybersecurity#
Blockchain technology introduces a paradigm shift in how we approach cybersecurity challenges. Its decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof nature has the potential to enhance data integrity, authentication processes, and secure transactions across various industries. By providing a robust foundation for trust and accountability, blockchain can pave the way for innovative solutions in cybersecurity.
However, it’s crucial to approach the adoption of blockchain with a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities and limitations. Scalability, regulatory considerations, privacy concerns, and the need for robust smart contract development are factors that must be carefully evaluated.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, it holds the promise of revolutionizing cybersecurity practices, mitigating risks, and fostering a more secure digital landscape for organizations and individuals alike.
