Windows Local Firewall Settings
Contents
Windows Local Firewall Settings#
A firewall serves as a protective barrier between your computer and potential threats from the internet. In the context of a Windows operating system, a local OS (Operating System) firewall is a fundamental component of your computer’s security infrastructure. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, helping to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard your sensitive information.
Understanding the Importance of a Local OS Firewall#
A local OS firewall acts as a gatekeeper, deciding which network traffic is allowed to enter or exit your computer. This is crucial for protecting your system from various online threats, such as viruses, malware, hackers, and other malicious activities. By filtering network traffic, a firewall helps to minimize the attack surface of your computer and provides an additional layer of defense.
Types of Windows Local OS Firewalls#
Windows operating systems come equipped with a built-in firewall solution that provides basic protection. There are two primary types of local OS firewalls in Windows:
Inbound Firewall: This type of firewall controls incoming network traffic. It examines incoming data packets and determines whether to allow or block them based on predefined rules. For instance, if you’re running a web server, the inbound firewall will only permit incoming web traffic (HTTP or HTTPS) while blocking other types of incoming connections.
Outbound Firewall: An outbound firewall regulates outgoing network traffic. It monitors the data leaving your computer and ensures that only authorized applications and services are allowed to communicate with external servers. For example, if a malicious program attempts to send data to a remote server, the outbound firewall can detect and block this unauthorized communication.
Configuring Windows Local OS Firewall Settings#
Configuring the Windows local OS firewall involves managing rules that determine how network traffic is handled. To access the firewall settings:
Open Control Panel: Go to the Control Panel from the Start menu or by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
Access Windows Defender Firewall: Within the Control Panel, click on “System and Security,” then select “Windows Defender Firewall.”
Manage Firewall Settings: From the left pane, click on “Advanced settings.” This will open the advanced settings window where you can configure various aspects of the firewall.
Inbound and Outbound Rules#
Within the advanced settings window, you’ll find options to create inbound and outbound rules. These rules dictate how the firewall treats different types of network traffic.
Inbound Rules#
Inbound rules control incoming traffic. By default, the Windows local OS firewall blocks all incoming connections and allows only those that match specific rules. For example, if you want to allow remote desktop connections, you can create an inbound rule that permits incoming traffic on the Remote Desktop protocol (usually port 3389).
Outbound Rules#
Outbound rules, on the other hand, manage outgoing traffic. They ensure that only approved applications can establish connections to external servers. This is particularly useful in preventing malware from sending sensitive information to malicious servers. For instance, you can create an outbound rule to allow your web browser to access the internet while blocking other applications from doing the same.
Creating Custom Rules#
While the Windows local OS firewall comes with predefined rules for common applications, you can also create custom rules tailored to your needs.
Rule Type: Choose whether you want to create an inbound or outbound rule based on the direction of network traffic you want to control.
Program or Port: You can either allow traffic for a specific program (executable file) or define a rule based on a specific port or range of ports.
Action: Decide whether to allow or block the traffic that matches the rule criteria.
Profile: Select the network profiles to which the rule applies. The three network profiles are Domain (when your computer is connected to a domain), Private (for home or work networks), and Public (for public places like coffee shops).
Name and Description: Provide a name and optional description for the rule to help you identify its purpose.
Monitoring and Notifications#
The Windows local OS firewall also allows you to monitor its activities and receive notifications about blocked or allowed connections.
Monitoring: In the advanced settings window, you can find a monitoring section that shows recent firewall activity. This can help you identify any unusual connection attempts.
Notifications: You can configure the firewall to notify you when it blocks a program from connecting or when there’s a security concern. These notifications can help you stay informed about potential threats.
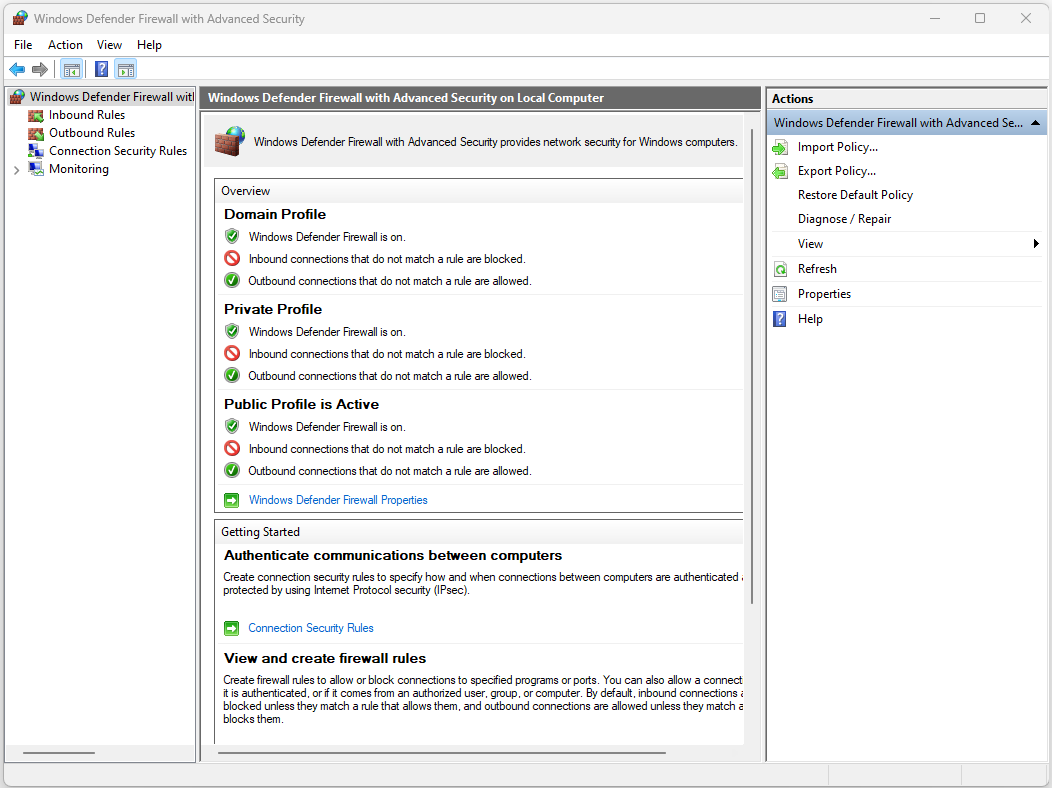
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security#
For users who require more advanced control over their firewall settings, Windows offers an even more comprehensive tool called “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.” This tool provides an extensive range of options for creating and managing firewall rules, connection security rules, and authentication methods.
Accessing Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
Open Run Dialog: Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
Type wf.msc into the Run dialog and press Enter. This will open the “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” window.
In this advanced tool, you can configure rules not only for inbound and outbound traffic but also for specific connection security and authentication settings. This is particularly useful for enterprises and advanced users who need fine-tuned control over their firewall’s behavior.
Final Words#
In a digital landscape where security threats are a constant concern, a Windows local OS firewall plays a vital role in safeguarding your computer. By regulating incoming and outgoing network traffic, it adds a crucial layer of protection against malicious activities. Understanding how to configure and manage your firewall rules empowers you to customize your computer’s defense mechanisms to suit your specific needs. Whether you’re a casual user or an advanced professional, the Windows local OS firewall is an indispensable tool in your cybersecurity arsenal.