BitLocker
Contents
BitLocker#
BitLocker is a disk encryption program developed by Microsoft. It is designed to provide enhanced security for the data stored on a computer’s hard drive or other storage devices. BitLocker works by encrypting the entire disk, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. This technology is primarily used in Windows operating systems, and it has been available since Windows Vista.
How Does BitLocker Work?#
BitLocker uses encryption algorithms to protect the data on a disk. When you enable BitLocker on a drive, it encrypts the entire contents of the drive, including the operating system, system files, and user data. This encryption process ensures that even if someone physically accesses the drive, they won’t be able to read its contents without the encryption key.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how BitLocker works:
Encryption: BitLocker encrypts the data on the drive using a symmetric encryption algorithm. This means that the same encryption key is used for both encryption and decryption.
Key Protection: To ensure the security of the encryption key, BitLocker offers multiple ways to protect it:
Password: You can set a password that must be entered at boot time to unlock the drive.
Smart Card: BitLocker can work with smart cards, which require the insertion of a physical card and a PIN for authentication.
TPM (Trusted Platform Module): Some computers have a TPM chip that securely stores the encryption key. BitLocker can use this chip for authentication, making it a convenient and secure option.
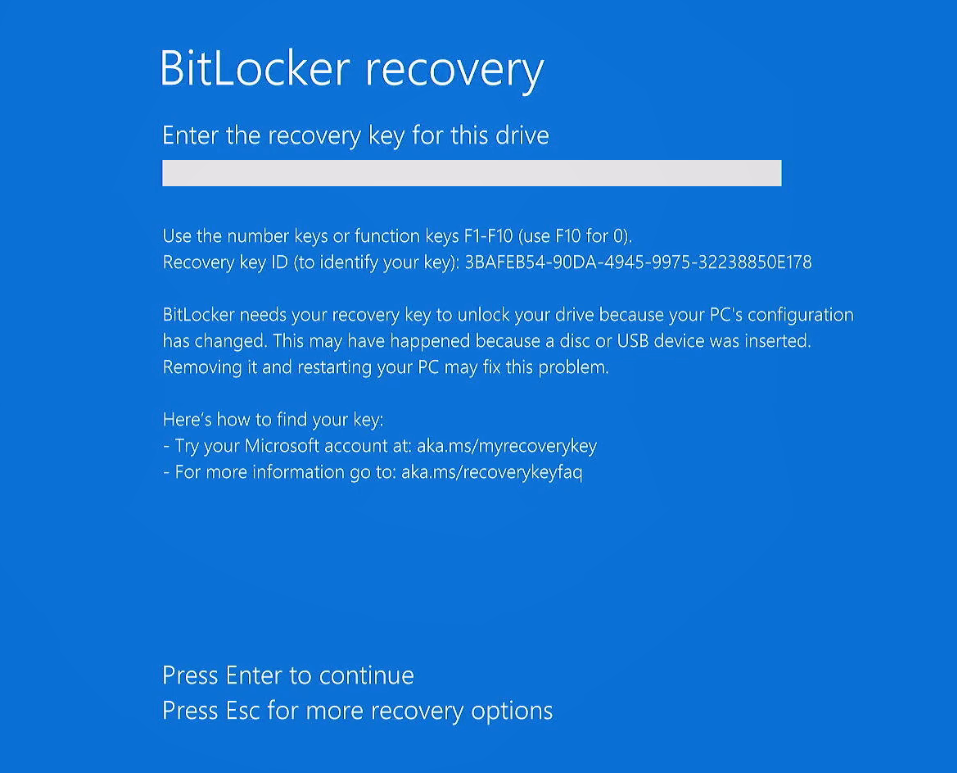
Recovery Key: In case you forget your password or encounter issues, BitLocker provides a recovery key, which is a 48-digit numerical code that can be used to unlock the drive. It’s essential to store this key in a secure location.
Decryption: When you start your computer, BitLocker prompts for authentication (e.g., password, smart card) or uses the TPM chip to unlock the encryption key. Once authenticated, the drive is decrypted, allowing the operating system to boot and access data.
Why Use BitLocker?#
BitLocker offers several benefits that make it a valuable tool for enhancing the security of your data:
Data Protection#
The primary purpose of BitLocker is to protect your data from unauthorized access. Even if your computer is stolen or someone attempts to access the hard drive directly, they won’t be able to read the data without the encryption key.
Full Disk Encryption#
BitLocker encrypts the entire disk, including the operating system and system files. This comprehensive encryption ensures that all data on the drive is secure, not just specific files or folders.
Seamless Integration with Windows#
BitLocker is seamlessly integrated into Windows operating systems, making it easy to set up and manage. There’s no need to install third-party software or tools.
Multiple Authentication Methods#
BitLocker offers flexibility in how you can authenticate to unlock your encrypted drive. You can choose from passwords, smart cards, or TPM-based authentication, depending on your security preferences and hardware capabilities.
Minimal Performance Impact#
Modern hardware and software optimizations have minimized the performance impact of BitLocker. In most cases, users won’t notice a significant decrease in system performance.
How to Enable BitLocker#
Enabling BitLocker on a Windows computer is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Prerequisites:#
You must be using a compatible version of Windows (e.g., Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11).
Your computer must have a TPM chip (Trusted Platform Module) or use alternative authentication methods.
Steps:#
Open Control Panel:
In Windows 10 or Windows 11, right-click the Start button, and select “Control Panel.”
In Windows 7 or Windows 8, open the Start menu and search for “Control Panel.”
System and Security:
Click on “System and Security” in the Control Panel.
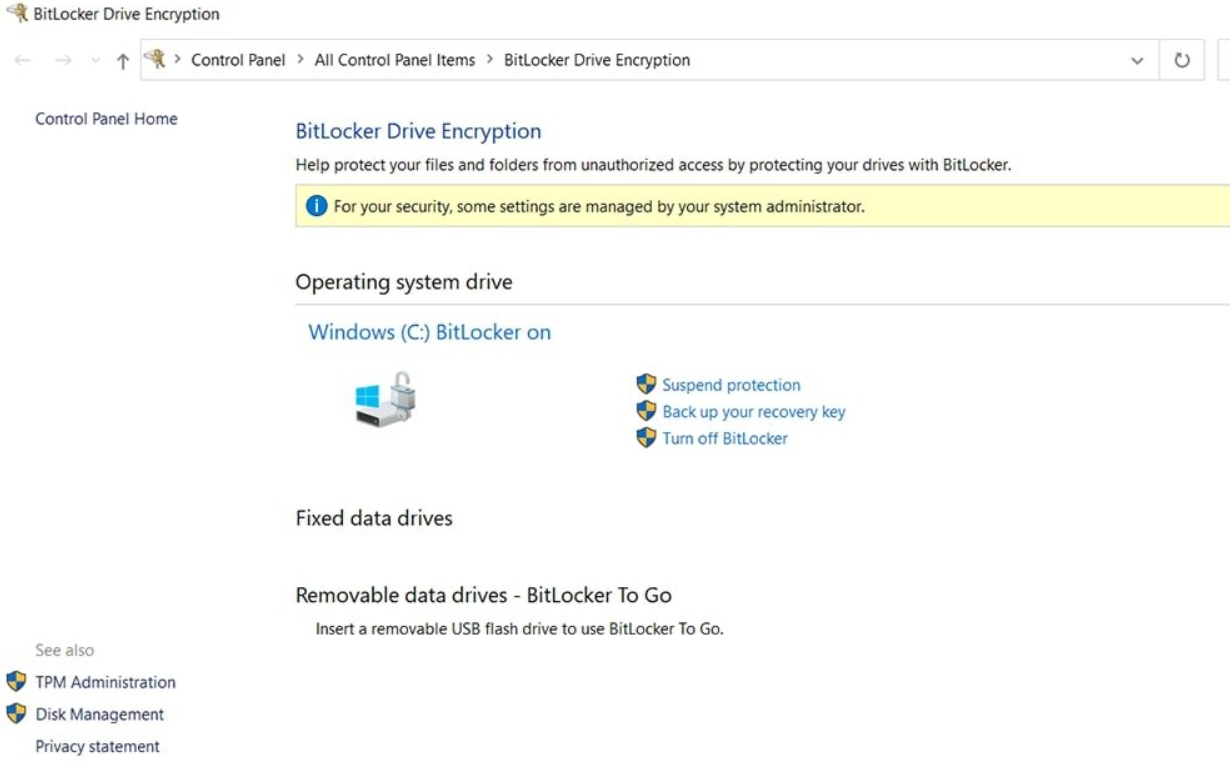
BitLocker Drive Encryption:
Under the “System and Security” category, you’ll find “BitLocker Drive Encryption.” Click on it.
Turn on BitLocker:
Locate the drive you want to encrypt and click on “Turn on BitLocker.”
Choose How to Unlock the Drive:
Select your preferred method of authentication (e.g., password, smart card, TPM). Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your chosen method.
Save or Print Recovery Key:
BitLocker will generate a recovery key. It’s crucial to save or print this key and keep it in a secure location. This key is your last resort to unlock the drive if you forget your password or encounter authentication issues.
Encryption Process:
BitLocker will start the encryption process, which may take some time, depending on the size of the drive and the performance of your computer.
Restart Your Computer:
After the encryption process is complete, you’ll be prompted to restart your computer. This is necessary to enable BitLocker on the drive.
Once you’ve completed these steps, your drive will be encrypted with BitLocker, and it will require authentication (e.g., password, smart card, TPM) to access its contents when you start your computer.
Managing BitLocker#
BitLocker provides several management options for users and administrators to ensure smooth operation and recovery in case of issues. Here are some key management tasks:
Changing the BitLocker Password or Authentication Method#
If you need to update your BitLocker password or switch to a different authentication method, you can do so through the BitLocker settings in the Control Panel. Simply follow the prompts to make the necessary changes.
Backing Up BitLocker Recovery Key#
It’s crucial to keep your BitLocker recovery key safe. You can back it up to a Microsoft account, a USB flash drive, or a file. This ensures that you can recover your data in case you forget your password or experience authentication problems.
Suspending BitLocker#
In some situations, you may need to temporarily suspend BitLocker protection, such as during a system update. BitLocker allows you to suspend protection and resume it when needed, without decrypting the entire drive.
Group Policy Management#
For businesses and organizations, BitLocker can be managed through Group Policy settings, allowing administrators to enforce specific policies and recovery options across multiple computers.
Typical Use Cases of BitLocker#
BitLocker is a versatile encryption tool that can be applied in various scenarios to enhance data security on Windows devices. Here are some typical use cases and scenarios where BitLocker can be valuable:
1. Laptop and Desktop Security in Business Environments#
Use Case: In a corporate environment, where sensitive business data is stored on laptops and desktops, BitLocker can be used to encrypt the entire hard drive. This ensures that if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized individuals, protecting sensitive company information.
Example: An employee’s work laptop is stolen from their car. Because BitLocker is enabled, the thief cannot access the data on the device without the encryption key or recovery key. The company’s confidential data remains secure.
2. Protection of Personal Data on Home Computers#
Use Case: BitLocker is not limited to business settings. Home users can also benefit from encrypting their personal computers to protect sensitive documents, photos, and financial information from unauthorized access.
Example: A family computer is used by multiple household members. BitLocker is enabled to safeguard personal files and documents. Even if a family member’s account is compromised, the encrypted data remains protected.
3. Securing Data on Portable Drives#
Use Case: BitLocker can be used to encrypt external USB drives and portable hard drives. This is particularly useful for storing sensitive files, backups, or confidential data that needs to be transported.
Example: An accountant uses an external hard drive to store financial records for clients. BitLocker encryption ensures that the data on the drive is secure, even if the drive is lost or stolen.
4. Protecting Data on Removable Media#
Use Case: BitLocker can be applied to protect data on removable media such as SD cards or flash drives. This is especially important for professionals who frequently use such media to transfer files.
Example: A photographer uses an SD card to store high-resolution images from a photo shoot. BitLocker encryption on the SD card prevents unauthorized access to these valuable photos.
5. Meeting Compliance Requirements#
Use Case: In industries where data security and regulatory compliance are critical, such as healthcare and finance, BitLocker can be used to meet encryption requirements mandated by regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
Example: A medical clinic uses BitLocker to encrypt patient records and medical history files. This ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations and protects patients’ sensitive health information.
6. Remote Work and Data Protection#
Use Case: With the rise of remote work, employees often store company data on their personal devices. BitLocker can be used to encrypt these devices, adding an extra layer of security to remote work setups.
Example: A remote worker uses a personal laptop to access company data. BitLocker encryption ensures that the company’s proprietary information remains confidential, even if the laptop is lost or stolen during travel.
7. Protection Against Insider Threats#
Use Case: BitLocker can help protect against insider threats, where employees with access to sensitive data may misuse it. Encryption ensures that even authorized users cannot access confidential information without proper credentials.
Example: An IT administrator at a financial institution has access to sensitive customer financial data. BitLocker is used to encrypt the administrator’s workstation, preventing unauthorized access to this critical information.
8. Enhancing Physical Security#
Use Case: In public places, such as libraries or shared workspaces, where you may leave your computer unattended for short periods, BitLocker can be used to secure your device from unauthorized access.
Example: A student studying at a university library steps away from their laptop briefly. BitLocker ensures that no one can access their files during their absence, even if the laptop is left unattended.
9. Protection Against Data Theft in Educational Institutions#
Use Case: Educational institutions, including schools and universities, can use BitLocker to secure student and faculty devices to protect sensitive educational records and research data.
Example: A university researcher’s laptop contains valuable research data. BitLocker safeguards the data from theft or unauthorized access, preserving years of research work.
10. Securing Virtual Machines#
Use Case: In virtualization environments where virtual machines (VMs) are used to run applications and services, BitLocker can be applied to protect VM disks. This is crucial for maintaining the security of virtualized workloads.
Example: A company runs critical services on virtual machines. BitLocker encryption is applied to the VM disks, ensuring the confidentiality of data processed by these virtualized services.
Final Words#
BitLocker is a valuable security feature in Windows operating systems that provides full disk encryption to protect your data from unauthorized access. It offers multiple authentication methods, minimal performance impact, and seamless integration with Windows. By following the simple steps outlined in this article, users can easily enable BitLocker on their computers and enhance the security of their data. Remember to keep your BitLocker recovery key safe, as it serves as a crucial backup to unlock your drive in case of password or authentication issues. BitLocker is an essential tool for safeguarding sensitive information, and its ease of use makes it accessible to both individual users and organizations seeking robust data protection.