Windows: Login Options
Contents
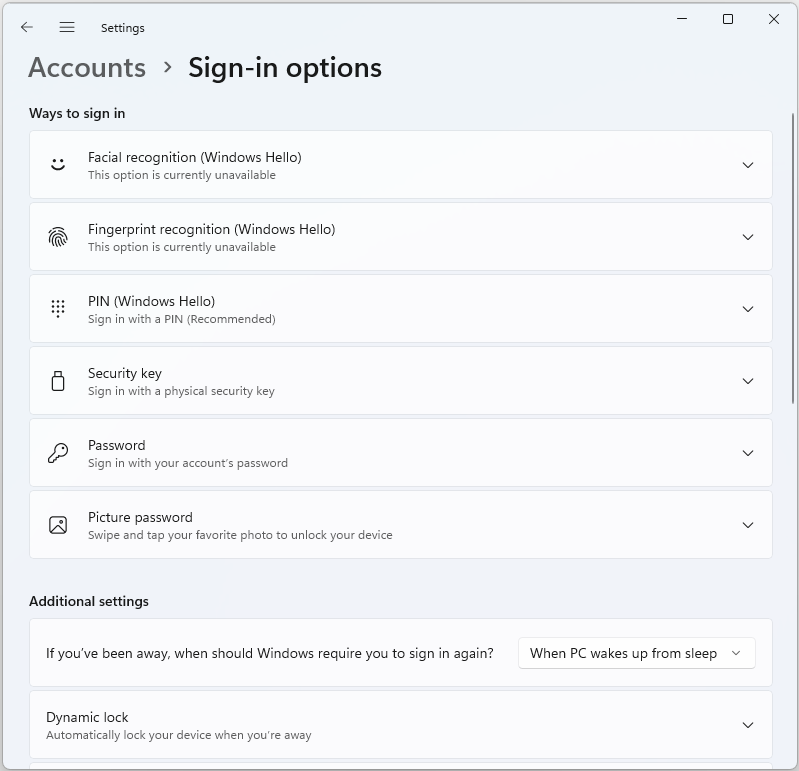
Windows: Login Options#
Windows operating system (OS) provides a variety of login options, each designed to cater to different user preferences and security needs. In this article, we will comprehensively discuss the key Windows login options, namely Password, Security Key, Picture Password, Facial Recognition (Windows Hello), Fingerprint Recognition (Windows Hello), and PIN. Let’s take a closer look at the primary Windows login options.
Password#
The password is a traditional and widely used method of logging into a Windows system. Users create a unique alphanumeric sequence as their password.
How it Works:
User enters their username.
User enters their password.
Windows verifies the entered credentials against stored records.
If they match, access is granted; otherwise, access is denied.
Use Cases:
Suitable for single-user systems and multi-user systems with distinct user accounts.
Provides a basic level of security.
Commonly used in personal computers and enterprise environments.
Example: When starting a Windows PC, users are typically prompted to enter their username and password.
Security Key#
A security key is a physical device that provides an additional layer of security when logging into Windows. It’s commonly a USB key or a Bluetooth-enabled device.
How it Works:
User inserts the security key into a USB port or activates it via Bluetooth.
Windows recognizes the key and verifies its authenticity.
If the key is authenticated, access is granted.
Use Cases:
Offers enhanced security by requiring a physical key for login.
Commonly used in high-security environments and by individuals who prioritize strong security measures.
Suitable for protecting sensitive data and systems.
Example: Users insert a security key into a USB port and tap it to confirm their identity when logging into Windows.
Picture Password#
Picture password is a unique and visually-based method of logging into Windows. Users choose a picture and create a series of gestures on it as their password.
How it Works:
User selects a picture from their gallery.
User draws a series of gestures (lines, circles, taps) on the chosen picture.
To log in, the user must recreate the gestures exactly as they were drawn during setup.
Use Cases:
Provides an alternative to traditional text-based passwords.
Offers a creative and personalized login method.
Suitable for touch-enabled devices and users who prefer a visual approach to security.
Example: Windows 8 and Windows 10 introduced the picture password feature, allowing users to draw on a favorite image to log in.
Facial Recognition (Windows Hello)#
Windows Hello offers facial recognition as an advanced login option. It uses a device’s camera to identify and authenticate the user based on their facial features.
How it Works:
The user looks at the device’s camera.
Windows Hello captures and analyzes facial features.
If the facial data matches stored records, access is granted.
Use Cases:
Offers a high level of security as it relies on unique facial characteristics.
Provides quick and convenient login, especially on laptops and tablets with integrated cameras.
Suitable for users who value both security and user experience.
Example: Many modern laptops come with built-in cameras and support Windows Hello facial recognition for seamless and secure logins.
Fingerprint Recognition (Windows Hello)#
Windows Hello also offers fingerprint recognition as a biometric login option. It uses a fingerprint scanner to authenticate the user.
How it Works:
The user places their finger on the fingerprint scanner.
Windows Hello reads and matches the fingerprint data with stored records.
If there’s a match, access is granted.
Use Cases:
Offers a high level of security as fingerprints are unique to each individual.
Provides quick and reliable login.
Commonly used on laptops and desktops equipped with fingerprint scanners.
Example: Many modern laptops come with fingerprint scanners that allow users to log in using their fingerprints.
PIN#
A Personal Identification Number (PIN) is a simplified alternative to traditional password-based login in Windows. Users create a numeric PIN, typically 4 to 6 digits long.
How it Works:
User enters their PIN.
Windows checks if the entered PIN matches the stored one.
If it matches, access is granted.
Use Cases:
Commonly used on touchscreen devices such as tablets and 2-in-1 laptops.
Offers faster login compared to a full password.
Suitable for devices with limited keyboard input.
Example: Many Windows tablets and laptops with touchscreens allow users to set up a PIN for login.
Importance of Windows Login Options#
Understanding and selecting the right login option in Windows is crucial for several reasons:
1. Security#
The choice of login method directly impacts the security of the system. Strong authentication methods like security keys, biometric recognition (facial and fingerprint), and traditional passwords offer different levels of security. Organizations and individuals can choose the appropriate method based on their security requirements.
2. User Experience#
The login process significantly affects the overall user experience. Windows provides a variety of login options to cater to different preferences. Methods like facial recognition and fingerprint recognition offer quick and seamless logins, enhancing user satisfaction.
3. Customization#
Windows login options allow for customization based on device type and user preferences. Users can select the method that aligns with their workflow and hardware, whether it’s the simplicity of a PIN on a tablet or the creativity of a picture password on a touchscreen device.
4. Data Protection#
In an era where data protection is paramount, the choice of login method plays a crucial role. Biometric methods and security keys offer strong protection against unauthorized access to personal and sensitive information.
5. Device Synchronization#
Certain login methods, such as Microsoft account login, enable synchronization of settings, apps, and preferences across multiple Windows devices. This provides a seamless and consistent user experience.
Final Words#
The login options available in Windows, including Password, Security Key, Picture Password, Facial Recognition (Windows Hello), Fingerprint Recognition (Windows Hello), and PIN, are designed to cater to a wide range of user preferences and security needs. Users and organizations should carefully consider their specific requirements when choosing a login method.
The importance of selecting the right login option cannot be understated. It impacts security, user experience, customization, data protection, and device synchronization. By making informed decisions about these options, users can strike a balance between security and usability, ensuring a seamless and secure computing experience in the Windows operating system.