Metered Connections in Windows
Contents
Metered Connections in Windows#
In the realm of modern technology, internet connectivity has become an integral part of our daily lives. However, there are instances where access to the internet might not be as stable or unlimited as we would prefer. In such cases, Windows operating systems offer a feature known as “Metered Connections” to help users manage their network usage effectively. In this article, we’ll delve into the concept of Metered Connections, explore their benefits, and also highlight their limitations.
What are Metered Connections?#
A metered connection, in the context of Windows operating systems, refers to a network connection that has its data usage measured and potentially limited by the user or the network provider. This feature is particularly useful for situations where users have limited data plans or want to conserve bandwidth. Windows allows users to designate specific network connections, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, as metered connections.
Benefits#
Metered Connections offer several benefits that can be advantageous in various scenarios. Let’s take a closer look at these benefits:
1. Data Usage Management#
One of the primary benefits of using Metered Connections is the ability to manage and control data usage effectively. By designating a connection as metered, Windows operating systems will prioritize essential updates and downloads, thereby reducing the consumption of data on non-essential tasks. This is particularly useful for users who have limited data plans or are using cellular networks with data caps.
Example: Consider a scenario where a user has a mobile hotspot connection with a limited data plan. By setting the hotspot connection as metered, the user can prevent automatic downloads of large files or updates, ensuring that their data allocation is used only for essential tasks.
2. Cost Savings#
Metered Connections can contribute to cost savings, especially for users who pay for data based on usage. By controlling the data-hungry activities and preventing unnecessary downloads, users can avoid exceeding their data limits and incurring additional charges from their ISP.
Example: A user who frequently travels and uses hotel Wi-Fi with limited free access can benefit from metering the connection. This ensures that bandwidth-hungry tasks are minimized, preserving the free data allowance for more critical tasks.
3. Improved Network Performance#
Metered connections can also contribute to improved network performance, especially in environments where multiple users are sharing the same network resources. By limiting data-intensive activities on a metered connection, such as streaming high-definition videos or downloading large files, you can help prevent network congestion and ensure that all users have a smoother online experience.
Example: Consider a scenario where a user is engaged in a video conference for work. Metering the connection will prevent background downloads from causing interruptions or lag during the video call, resulting in a smoother and more productive experience.
4. Control Over Updates#
Windows operating systems frequently release updates to enhance security, stability, and functionality. However, these updates can be substantial in size and may consume a significant amount of data. Metered Connections allow users to exercise greater control over when and how updates are downloaded and installed.
Example: A user who is about to embark on a journey and intends to use a limited mobile data connection can postpone non-essential updates until they have access to a more stable and unlimited network.
Limitations#
While Metered Connections offer several advantages, it’s important to acknowledge their limitations as well. Here are some limitations to consider:
1. Delayed Updates#
While delaying updates can be beneficial for managing data usage, it may also result in delayed security patches and critical bug fixes. By postponing updates, users could potentially expose their systems to vulnerabilities that could have been mitigated through timely updates.
Example: If a user consistently postpones updates on a metered connection, they might miss out on crucial security patches that protect their system from emerging threats.
2. Limited Functionality#
Some applications and features rely on continuous and unrestricted internet access. When a connection is designated as metered, certain functionalities might be limited or disabled, impacting the user experience.
Example: Cloud-based applications that rely on real-time synchronization may not function optimally on a metered connection due to limited data availability.
3. Background Tasks#
While the operating system prioritizes essential updates on metered connections, background tasks and downloads may still occur to some extent. These tasks could contribute to data consumption and potentially affect network performance.
Example: Even with a metered connection, background tasks such as email synchronization and app updates could still consume a portion of the available data.
4. Manual Configuration#
Configuring a connection as metered requires manual intervention by the user. This might be inconvenient for individuals who prefer a more automated approach to managing their network usage.
Example: Users who frequently switch between different networks might find it cumbersome to remember to configure each connection as metered whenever necessary.
Setting Metered Connections#
Configuring metered connections in Windows allows you to manage your data usage and prioritize essential tasks over background activities.
Windows 10#
Open Network Settings: Click on the Start menu and select “Settings” (the gear icon). In the Settings window, click on “Network & Internet.”
Select the Desired Connection: Under the “Network & Internet” settings, choose “Wi-Fi” or “Ethernet,” depending on the connection you want to set as metered.
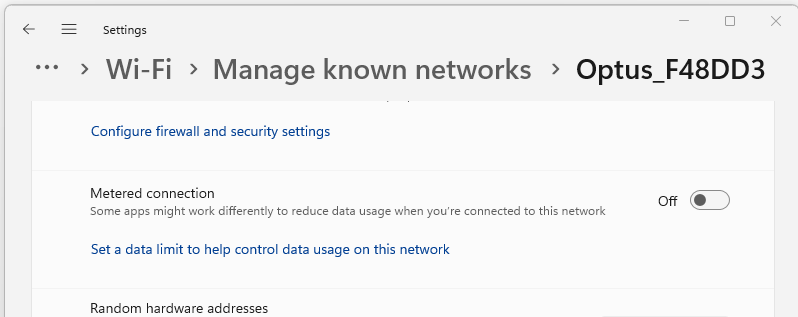
Manage Known Networks: Scroll down and click on “Manage known networks.” This will display a list of all the Wi-Fi networks you’ve connected to previously.
Choose a Network: Select the Wi-Fi network you want to set as metered. Click on it to reveal the network details.
Set as Metered Connection: Toggle the switch under the “Metered connection” option to the “On” position. This designates the selected Wi-Fi network as a metered connection.
Confirmation: A small note will appear under the network name, indicating that it is now a metered connection.
Repeat for Other Networks: If you have multiple Wi-Fi networks you want to set as metered, repeat the process for each network.
Windows 11#
Access Network & Settings: Click on the Start menu and select “Settings” (the gear icon). In the Settings window, click on “Network & internet.”
Choose Wi-Fi or Ethernet: Under “Network & internet” settings, select “Wi-Fi” or “Ethernet,” depending on the connection type you want to set as metered.
View Available Networks: Click on “Advanced network settings” to view the available networks.
Select Network Properties: Choose the Wi-Fi network you want to set as metered and click on “Properties.”
Toggle Metered Connection: Under the network properties, toggle the switch for “Metered connection” to the “On” position.
Save Changes: Click the “Save” button to apply the changes.
Repeat for Other Networks: If you have additional networks to set as metered, go back to the list of available networks and repeat the process.
Final Words#
In the realm of digital connectivity, Metered Connections offer a valuable solution for individuals seeking to manage their data usage effectively, control costs, and optimize network performance. By designating specific connections as metered, users can strike a balance between staying connected and avoiding excessive data consumption. However, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the limitations. While metering connections can provide advantages such as data usage management and cost savings, users should also be mindful of potential drawbacks, such as delayed updates and limited functionality.