Network Topologies
Contents
Network Topologies#
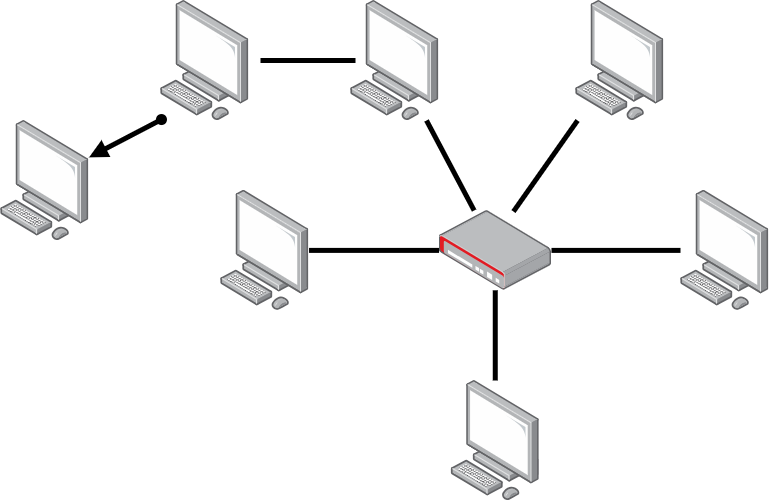
Network topology refers to the arrangement of devices and the interconnection scheme used in a computer network. These topologies play a critical role in how data is transmitted and how devices communicate with each other. In this article, we will comprehensively discuss various network topologies, including point-to-point, bus, ring, token ring, star, mesh, and hybrid topologies.
Point-to-Point Topology#
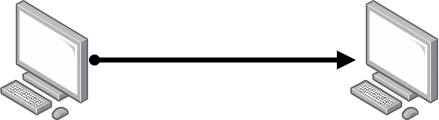
Point-to-point topology is the simplest form of network topology. In this configuration, two devices are directly connected to each other using a dedicated communication link. It is often used in scenarios where only two devices need to communicate.
Advantages of Point-to-Point Topology:
Simplicity: It’s easy to set up and configure.
Dedicated Connection: The link is exclusively reserved for communication between the two connected devices.
Disadvantages of Point-to-Point Topology:
Limited Scalability: Adding more devices requires additional dedicated links, making it impractical for larger networks.
Example: Connecting two remote offices using a leased line is an example of point-to-point topology.
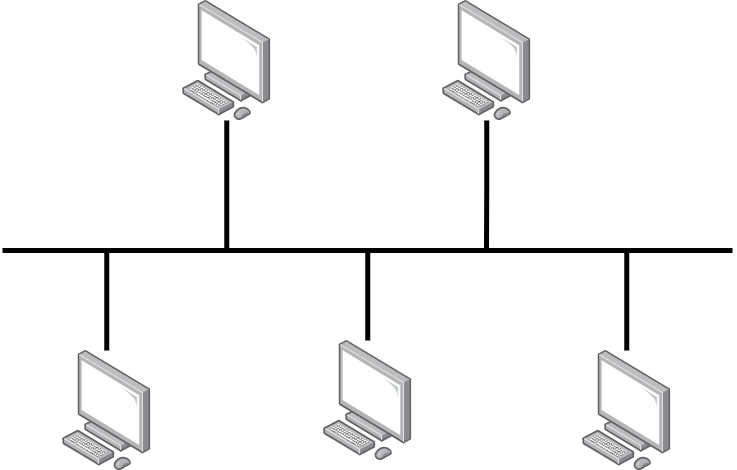
Bus Topology#
Bus topology is a linear network configuration where devices are connected to a central cable, known as the bus or backbone. Data is transmitted along the bus, and each device on the network receives the data. Devices check the data to determine if it’s intended for them.
Advantages of Bus Topology:
Simplicity: It’s easy to install and set up.
Cost-Effective: Requires less cabling compared to other topologies.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:
Single Point of Failure: If the central cable is damaged, the entire network can be disrupted.
Limited Scalability: Adding new devices can be challenging and may require modification of the central cable.
Example: Legacy Ethernet networks, such as 10BASE2 and 10BASE5, used bus topology.
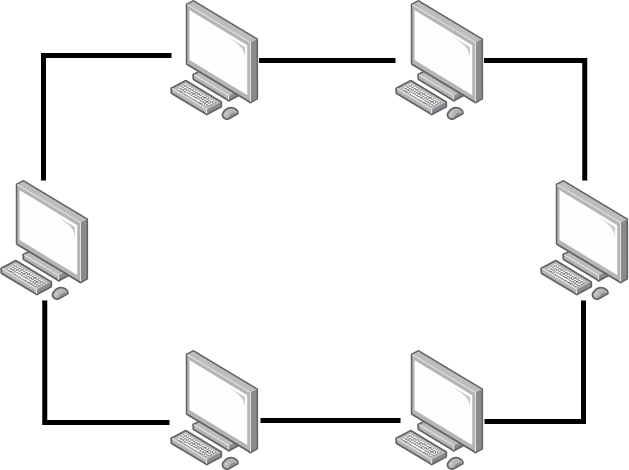
Ring Topology#
In a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed-loop configuration. Each device is connected to exactly two other devices, forming a ring. Data travels in one direction around the ring until it reaches its destination.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
Equal Data Sharing: Each device has an equal opportunity to access the network, leading to fair data distribution.
Simple Wiring: Requires less cabling than a star topology.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
Single Point of Failure: If one device or cable fails, it can disrupt the entire network.
Slower Performance: Data must circulate through the entire ring before reaching its destination, potentially leading to latency.
Example: Token Ring networks used ring topology. However, they are now largely obsolete, replaced by Ethernet.
Token Ring Topology#
Token Ring topology is a specific type of ring topology where devices are connected in a physical ring, and data is transmitted sequentially from one device to another. In Token Ring networks, a special token is passed from device to device, allowing the device holding the token to transmit data.
Advantages of Token Ring Topology:
Deterministic: Provides predictable and consistent network performance.
Collision-Free: Token passing ensures that only one device can transmit at a time, reducing collisions.
Disadvantages of Token Ring Topology:
Complexity: Setting up and managing Token Ring networks can be complex.
Limited Scalability: Adding new devices to the ring can be challenging.
Example: Token Ring networks were once used in some corporate environments for their deterministic performance.
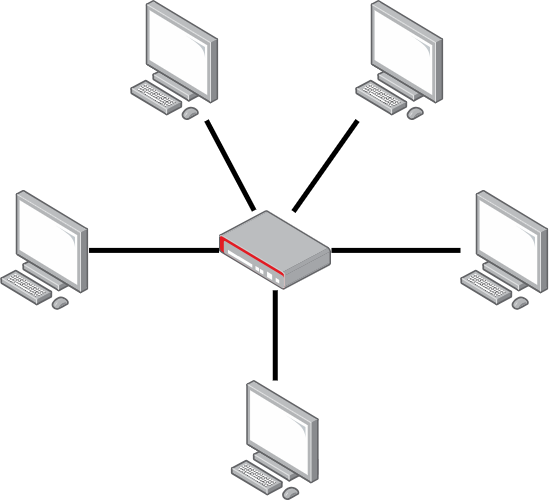
Star Topology#
Star topology is one of the most common network topologies. In this configuration, all devices are connected directly to a central hub or switch. This central hub acts as a traffic controller, ensuring efficient data transmission between devices.
Advantages of Star Topology:
Reliability: If one cable or device fails, only that specific connection is affected, leaving the rest of the network operational.
Easy to Manage: Adding or removing devices is straightforward since they connect directly to the central hub.
Isolation: Each connection is isolated, preventing data collisions between devices.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
Single Point of Failure: If the central hub fails, the entire network goes down.
Cost: Implementing a star topology can be more expensive due to the need for a central hub and individual cables.
Example: Many modern Ethernet LANs (Local Area Networks) use a star topology. Each computer in an office connects to a central Ethernet switch.
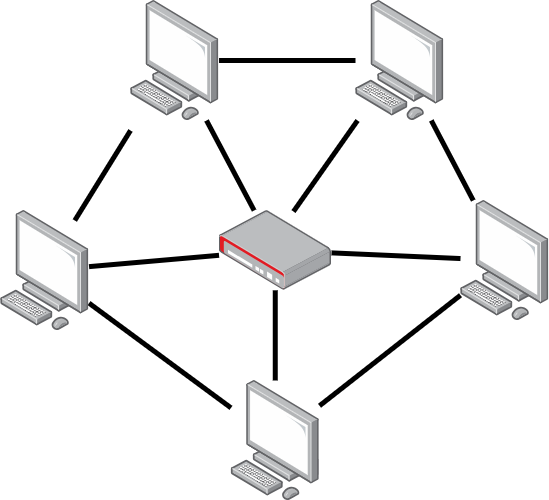
Mesh Topology#
Mesh topology is a network architecture where each device is connected to every other device. This creates a redundant and self-healing network where data can take multiple paths to reach its destination.
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
High Reliability: Multiple paths for data transmission enhance network reliability.
Scalability: Easy to expand by adding more devices to the mesh.
Self-Healing: If one node fails, the network can automatically reroute traffic.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
Complexity: Setting up and configuring a mesh network can be complex.
Cost: The need for multiple devices can be expensive.
Example: Some smart home systems, like those for lighting or security, use mesh networks to ensure reliable communication between devices.
Hybrid Topology#
Hybrid topology is a combination of two or more different network topologies. Organizations often use hybrid topologies to meet their specific network requirements. For example, a network could be a combination of star and mesh topologies to balance reliability and scalability.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
Customization: Organizations can tailor the network to meet their specific needs by combining different topologies.
Optimization: Hybrid topologies can provide the best of both worlds in terms of reliability and scalability.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
Complexity: Managing a hybrid network can be more complex due to the different topology components.
Cost: The cost of implementing and maintaining a hybrid topology can vary depending on the components used.
Example: A large corporation might use a hybrid topology, where its headquarters employs a star topology for office LANs, while remote branches use a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint topology to connect to the main office.
Comparison Table#
Here’s a comparison table that highlights the main attributes of point-to-point, bus, ring, token ring, star, mesh, and hybrid topologies:
Topology |
Description |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Point-to-Point |
Direct connection between two devices. |
Simplicity |
Limited scalability |
Connecting remote offices |
Bus |
Linear connection of devices to a central bus. |
Simplicity, cost-effective |
Single point of failure, limited scalability |
Legacy Ethernet networks |
Ring |
Devices connected in a closed-loop. |
Equal data sharing, simple wiring |
Single point of failure, slower performance |
Token Ring networks (obsolete) |
Token Ring |
Ring topology with token-based data transfer. |
Deterministic, collision-free |
Complexity, limited scalability |
Some legacy corporate networks |
Star |
Devices connected to a central hub/switch. |
Reliability, easy management, isolation |
Single point of failure, cost (central hub/switch) |
Modern Ethernet LANs |
Mesh |
Devices connected to every other device. |
High reliability, scalability, self-healing |
Complexity, cost (multiple devices) |
Smart home systems, critical apps |
Hybrid |
Combination of two or more topologies. |
Customization, optimization |
Complexity, cost (varies with components) |
Tailored network solutions |
Please note that the suitability of a particular topology depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the network being designed.
Final Words#
Selecting the appropriate network topology is a critical decision when designing a computer network. Each topology has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for specific use cases. The choice of network topology should align with the organization’s needs, budget, and performance requirements. A well-designed topology is the foundation of a robust and efficient computer network.